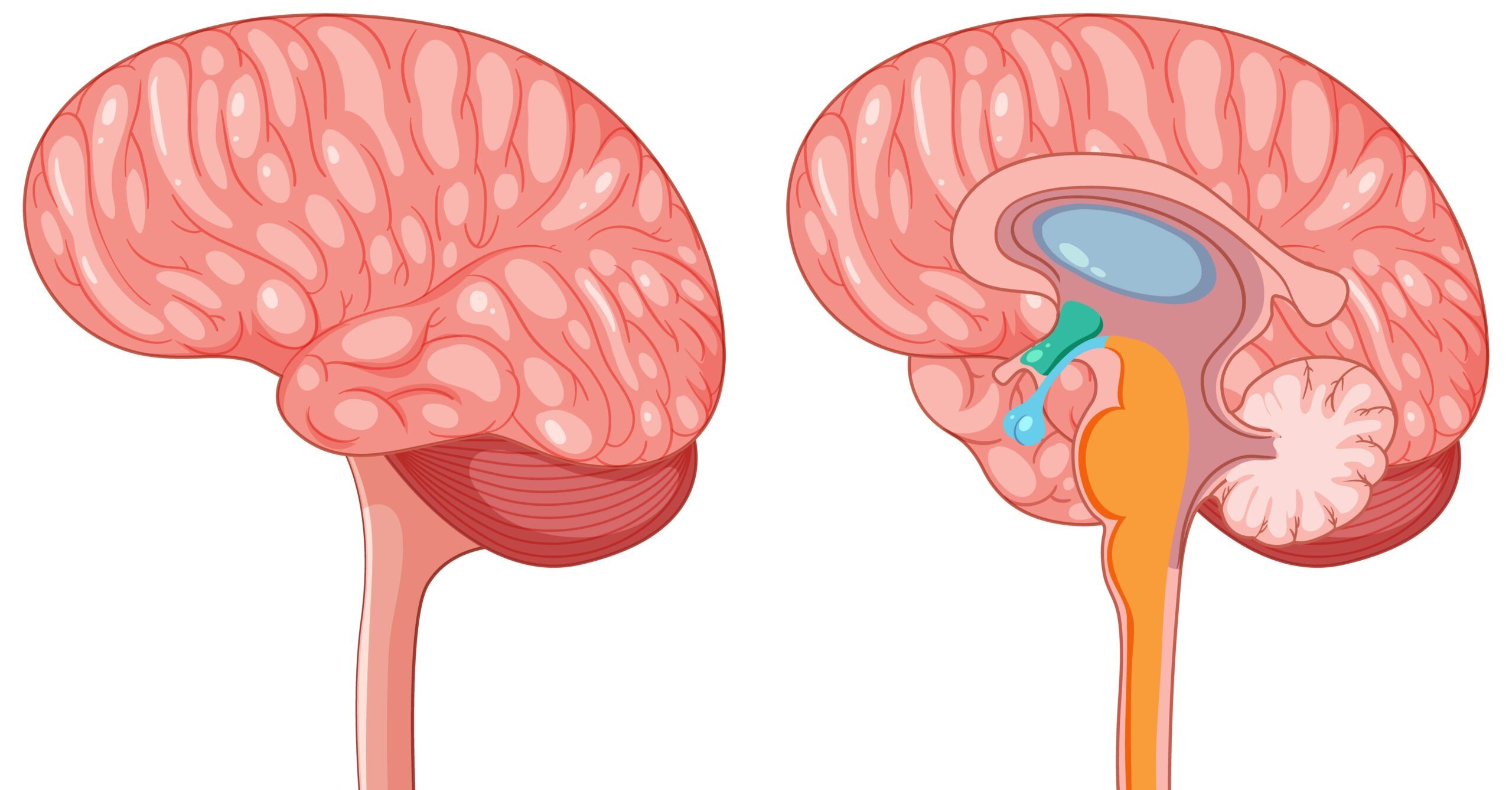
Hydrocephalus, also known as water in the brain, is a neurological disorder. When the circulation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are obstructed by the ventricles and arachnoid villi of the brain, it can occur. This mainly happens when the intracranial pressure (ICP) level of the brain is increased from its normal rate i.e. between 5-10mm Hg. Because of this ventricle infection, the buildup of fluid puts pressure on the brain, which can damage it. Common symptoms of hydrocephalus may include enlargement of the head, irritability, and vomiting.
It can affect all age groups, including children, infants, and old adults.

Hydrocephalus mainly has two types:
- Communicating Hydrocephalus:
Communicating hydrocephalus is also known as non-obstructive hydrocephalus. It occurs when there is an obstruction in the ventricular system of the brain and its arachnoid villi doesn’t reabsorb cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) but ventricles still circulate the fluid. This impairment in the reabsorption of CSF leads to its accumulation and increased pressure.
2. Non-communicating Hydrocephalus:
Non-communicating hydrocephalus, also known as obstructive hydrocephalus, occurs when the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is blocked along one or more of the passages connecting the ventricles of the brain.
Causes of Hydrocephalus
It can be congenital means beginning at and continuing since birth or acquired later in life. Mainly, it depends on the mechanism of your skull.
· Excess production: Too much production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in epithelial cells of the ventricular system creates hyperfunctioning tumours of the choroid plexus.
· Abnormal circulation: Unusual circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) due to its blockage by the 2nd ventricle of the brain called form foramen of Monro.
· Unusual Absorption: Bleeding within the brain due to brain haemorrhage, often caused by trauma or stroke can disrupt the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
· Infection: Meningitis, a bacterial or viral infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can block or impair cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
· Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH): It is an atypical buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain of the ventricular system.
Some Common Signs in Infants, Older Children & Adults
Hydrocephalus symptoms in different age groups:
1. In Infant
· Head enlargement
· Sleepiness
· Frontal Bossing
· Poor Feeding
· Poor Growth
· Sunsetting eyes sign

2. In older children and adults
· Awakening due to headache
· Nausea and Emesis
· Poor growth
· Memory problem
· Vision problem
Diagnosis and Treatments of Hydrocephalus
For diagnosis of congenital hydrocephalus, a routine prenatal ultrasound scan may detect the condition during pregnancy. If an ultrasound scan shows any abnormality, further tests are ordered.
For acquired hydrocephalus, the diagnostic technique usually includes a medical examination by doing a CT scan and an MRI scan to detect possible tumours or lesions in the brain.

The goal of treatment is to relieve the pressure on the brain and manage underlying. The standard treatment option includes:
1. Shunt placement:
It is a surgical procedure commonly used to treat hydrocephalus. In this surgical procedure, the medical team thoroughly evaluates the individual’s health and neurological condition by conducting an MRI scan and CT scan to determine the best location for placing the shunt.
A shunt is a tiny tube that helps to divert and regulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain. It can be effective in managing hydrocephalus.
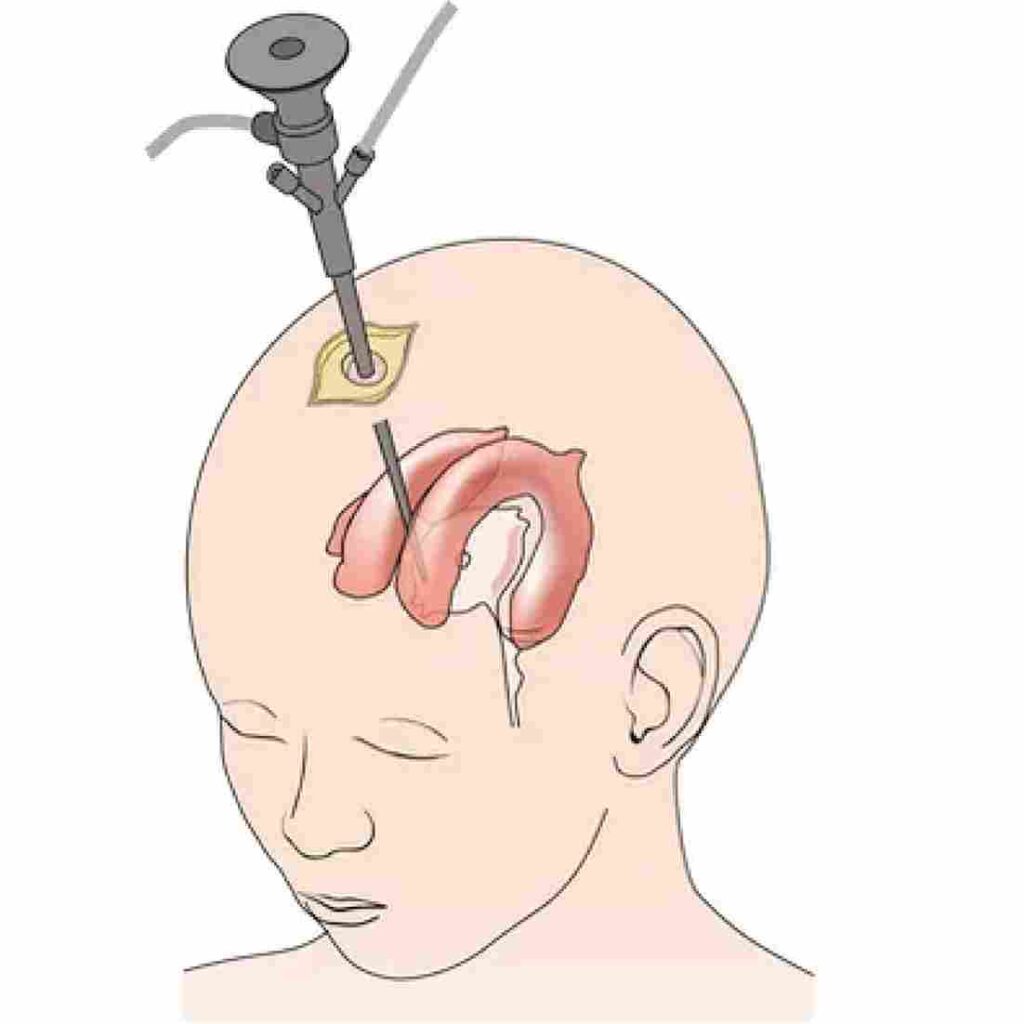
2. Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV):
In this surgical procedure, the endoscope is passed through a small opening in the skull into the ventricles of the brain. It involves creating a new pathway for CSF flow and this path allows it to bypass the obstruction and flow freely.
3. Medication:
Medication is a temporary measure of hydrocephalus. In certain situations, medication may be prescribed to reduce CSF problems of circulation, and absorption and helps to reduce the hydrocephalus symptoms.
Conclusion
Hydrocephalus is a complex neurological condition. It involves abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow in the ventricular system of the brain which can lead to various symptoms. Recognizing the sign of hydrocephalus is essential as it needs immediate medical attention. It is crucial to reach out to a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. Remember early diagnosis and treatment is the key to preventing complications.