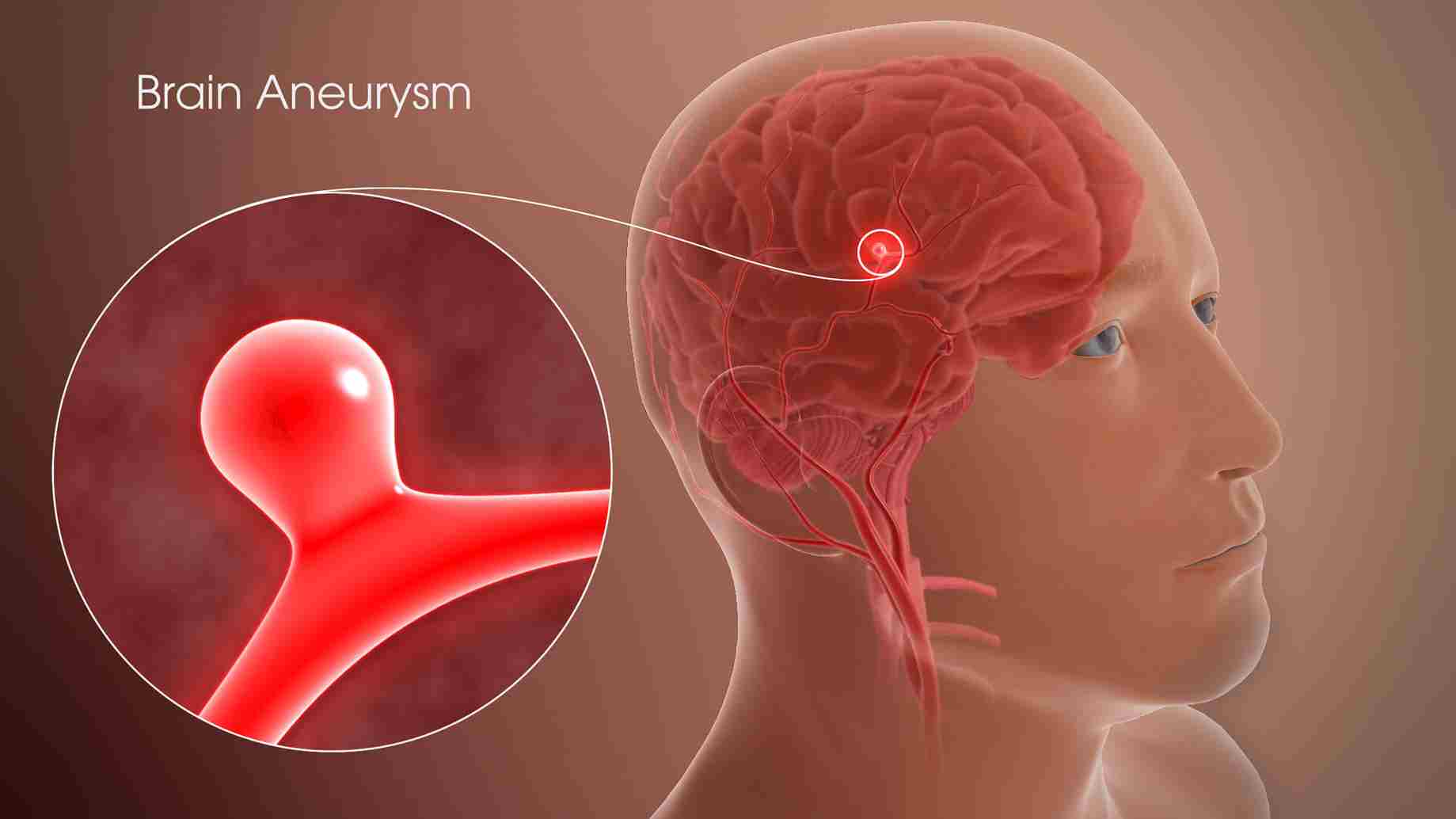
Brain aneurysms, also called cerebral aneurysm is an abnormal bulging in the weak area of the artery in or around the brain. It is a deformity of an artery where the balloon-like bulge fills with blood and, when developed, can even lead to serious brain injuries or strokes.
Brain aneurysms can occur anywhere in the brain, but they mostly form in the major arteries along the base of the skull. It is a life-threatening condition that can affect anyone and at any age, but mostly affects people between the ages of 30 and 60.
Important Types of Presentation of Brain Aneurysms:
Ruptured Brain Aneurysm: A ruptured brain aneurysm occurs when the aneurysm bursts, leading to bleeding in the brain. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention.
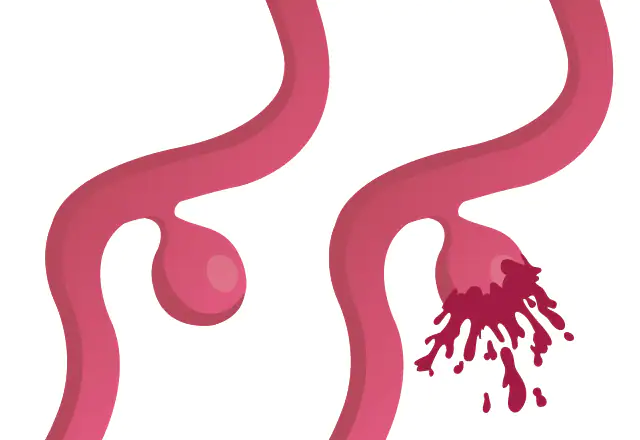
Unruptured Brain Aneurysm with Mass Effect: An unruptured brain aneurysm refers to an aneurysm that has not yet burst. However, it can still cause symptoms and pose a risk.
What Are the Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms?
Mostly brain aneurysms do not show any symptoms until they are developed and become large, and start to leak blood or burst. If it starts affecting surrounding nerves and tissues, it can cause signs and symptoms that include the following.
Symptoms of an unruptured brain aneurysm:
– Weakness
– Changes in vision
– A dilated pupil
– Pain above and behind the eye
Symptoms of a ruptured brain aneurysm
– A sudden & severe headache
– Sensitivity to light
– Dropping eyelid
– Pain above and behind the eye
– Feeling of weakness or numbness
– Loss of consciousness
– Neck stiffness
– Trouble walking or dizziness
– Blurry or double vision
Brain Aneurysms Treatment Options and New Techniques:
- Observation– In some cases, especially when the unruptured aneurysm is small and not causing symptoms, the neurosurgeon may recommend regular monitoring through imaging tests. This approach involves observing the aneurysm over time to detect any changes or growth.
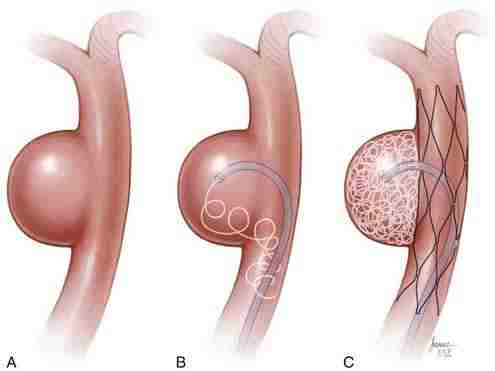
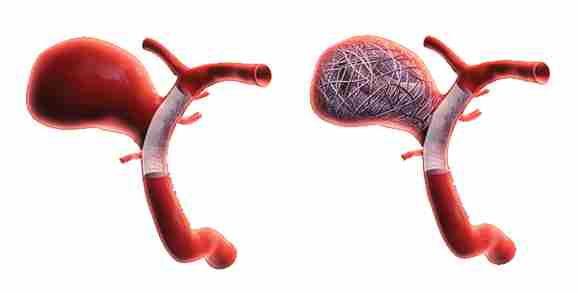
- Endovascular Coiling– Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat brain aneurysms. It involves inserting a catheter into the affected blood vessel and placing small coils inside the aneurysm. These coils promote blood clotting and effectively seal off the aneurysm, reducing the risk of rupture.

- Endovascular Stents– In certain cases, endovascular stents may be used in conjunction with coil placement for the treatment of brain aneurysms. A stent is a small tube-like device that is inserted into the affected blood vessel. It is designed to provide structural support and hold the coils in place within the aneurysm.
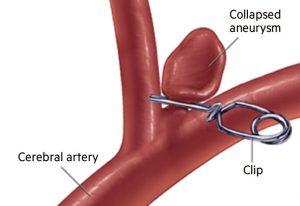
- Surgical Clipping – Clipping is a surgical procedure performed to treat brain aneurysms. It involves making a small opening in the skull to access the aneurysm and placing a tiny metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to stop blood flow and prevent rupture.
- Flow Diversion– This is an advanced technique used to treat complex and large aneurysms. It involves placing a stent-like device called a flow diverter across the neck of the aneurysm. This device redirects blood flow away from the aneurysm, promoting the formation of a clot and effectively sealing off the aneurysm.
CONCLUSION
A brain aneurysm is a condition that occurs when the blood vessels in the brain become weak or bulge out. Symptoms of brain aneurysm vary according to the condition of the aneurysm such as unruptured, ruptured or leaking.
If you have any symptoms related to brain aneurysms, it’s essential to consult with a neurosurgeon specializing in brain aneurysms to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on the specific characteristics of the aneurysm. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications associated with brain aneurysms.
(Also Read: Hydrocephalus Symptoms: What is It, Diagnosis and Treatment (drprashantneurosurgeon.com))