Understanding Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that involves implanting a device, similar to a pacemaker, to send electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. These electrical impulses help to regulate abnormal brain activity, effectively improving symptoms of various neurological disorders.
Deep Brain Stimulation aims to restore normal brain function by stimulating specific areas of the brain that control movement, emotions, and other vital functions.
What is Deep Brain Stimulation?
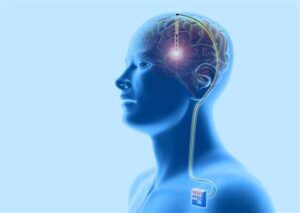
In the world of neurology and neurosurgery, few treatments are as groundbreaking and transformative as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). For those suffering from neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia, DBS offers a lifeline—a way to manage symptoms that once seemed insurmountable. But what exactly is DBS, how does it work, and why has it become such an essential tool in treating brain disorders?
In this blog, we’ll dive into the science, the procedure, and the profound impact DBS has had on countless patients around the globe.
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work?
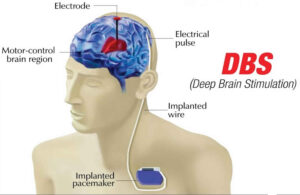
At the core of DBS is a neurostimulator, often referred to as a “brain pacemaker.” This device is surgically implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone, with wires running from it to specific areas of the brain that need stimulation. The most commonly targeted regions for DBS include the subthalamic nucleus and the globus pallidus internus, areas involved in motor control.
Once the electrodes are in place, the device is programmed to send electrical impulses to these targeted areas. These electrical signals can be adjusted in terms of frequency, intensity, and duration to optimize their therapeutic effect. Unlike other brain surgeries, DBS is not intended to cure the disease, but rather to manage symptoms, allowing patients to regain control over their daily lives.
The beauty of DBS lies in its ability to be adjusted over time. If a patient’s symptoms change or evolve, their doctor can fine-tune the settings on the neurostimulator to better address their needs. This ability to modify the treatment allows for a level of flexibility that makes DBS a highly effective, personalized treatment option.
Conditions Treated with Deep Brain Stimulation
Here are some of the most common conditions treated with DBS:
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Essential Tremor
- Dystonia
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation
The benefits of DBS can be life-changing for many patients. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Quality of Life
- Reduction in Medication
- Adjustable Treatment
- Minimally Invasive
The Future of DBS
The future of DBS holds exciting possibilities. Ongoing research is exploring the potential of DBS for treating a wider range of neurological and psychiatric conditions. Advances in personalized medicine, including the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize DBS settings, may lead to even better outcomes for patients.
Moreover, researchers are working on developing smaller, more efficient devices, reducing the need for invasive procedures. In the future, DBS may become even more accessible, offering relief to more people suffering from neurological conditions worldwide.
Conclusion
Deep Brain Stimulation is one of the most revolutionary treatments in the field of neurology, offering hope to individuals who have struggled with debilitating neurological conditions for years. By using electrical impulses to regulate brain activity, DBS has transformed the lives of countless patients, allowing them to regain control over their movements and daily lives. With ongoing advancements in technology and research, the future of DBS is bright, promising even greater possibilities for managing neurological and psychiatric disorders. Whether you or a loved one is considering DBS, it’s clear that this procedure has opened up new doors for those seeking a better quality of life.